A solar panel system can power your home through clean, low-cost electricity for decades
Home solar panel systems are becoming more popular in the United States, from California to Connecticut. Residential solar offers homeowners the opportunity to save money on utility bills and live sustainably.
But some homeowners might wonder — how much energy do solar panels produce? Solar is an investment and the amount of money you save is directly tied to the amount of energy solar panels offset.
Key Summary Box
- New, residential solar panels can produce between 370-415 W per peak sunlight hour
- Home solar panel systems can power all or most of your home’s energy needs
- Many homeowners chose solar to produce their own energy and reduce their utility bills
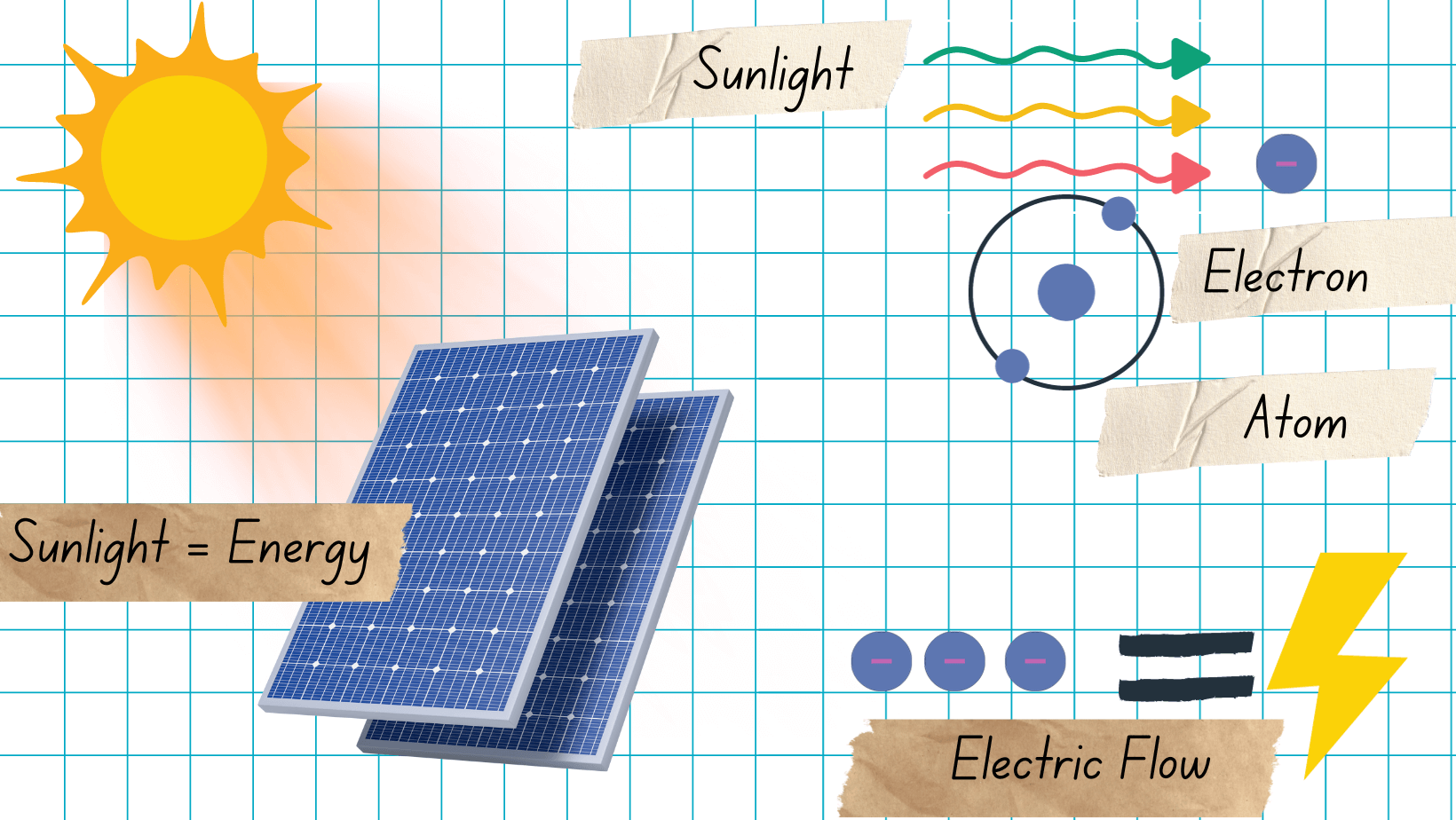
How do solar panels produce electricity?
Don’t be afraid of science or technology, it’s easy to understand the basic process of solar energy. Solar panels utilize the photovoltaic effect to produce electricity. Solar panels are made of semiconductor materials — like silicon — which interact with sunlight.
When sunlight — consisting of particles called photons — hits the semiconductor material, it “knocks” electrons off of atoms. This “knockoff” effect creates a flow of electrons, which is electricity.
Solar panels are made up of multiple solar cells, which are typically crystalline silicon. Solar cells absorb sunlight and create usable electricity. This process is called the photovoltaic effect, which is why solar panels are sometimes called photovoltaic (or PV) modules.
Important solar energy terms, explained
What is a watt?
A watt (W) is a unit of power in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of electrical power, a watt is the rate at which energy is used or produced. It is a measure of how quickly electrical work is done. For example, if an electrical device has a power rating of 100 watts, it means that the device consumes or produces 100 joules of energy every second.
In the context of solar panels, the power output is often measured in watts or kilowatts, representing the amount of electrical power the panels can generate under specific conditions.
What is a kilowatt?
A kilowatt (kW) is the equivalent of one thousand watts and is a unit of measurement to quantify the capacity or output of a solar system. The kilowatt is a standard unit for expressing the rate at which energy is produced or consumed.
When referring to solar panels or solar installations, the term kilowatt is often used to describe the system’s capacity or size. For example, a residential solar panel system might be rated at 5 kW, meaning it can produce 5 kilowatts of power under specific conditions, typically measured in full sunlight.
What is a kilowatt-hour?
The total energy produced over time is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). If the 5 kW solar panel system operates at its full capacity for one hour, it would generate 5 kWh of electricity. Kilowatt-hours measure the total energy produced by solar panels or consumed by your home over time.

How much energy does a solar panel produce?
A new residential solar panel can typically produce between 370-415 watts per hour — assuming there is direct sunlight. This number can vary based on multiple factors, including panel age, amount of sunlight, weather and other factors.
To calculate how much electricity a solar panel can produce in one day, you need a few numbers:
- The power output or power rating of one solar panel (measured in watts)
- The number of peak sunlight hours in your area (measured in hours)
The equation is simple, you multiply the power output of your solar panels by the number of peak sunlight hours to get an estimate of how much electricity a solar panel produces.
If your one solar panel produces 400 W and your area gets four peak sunlight hours — your equation is 400 W x 4 hrs.
The answer would be 1,600 watts per hour (Wh) or 1.6 kWh. However, solar panels lose some energy when converting solar-generated alternating current (AC) to household appliance direct current (DC). The amount of energy lost is usually between 2-5%.
How much energy will my solar panel system produce in a day?
This is another simple equation to get an estimate. Remember, this number won’t be totally accurate due to wiring and inverter energy loss, weather conditions and age.
Take the equation above, using the power output of a solar panel multiplied by the number of peak sunlight hours in a day. You’re going to multiply this number by the amount of solar panels on your rooftop.
Using the previous example, if you have solar panels that produce 400 watts per hour, live in an area with four peak sunlight hours and have 10 solar panels on your roof — your equation will be 400 W x 4 hrs x 10 panels.
The estimated amount of energy your system will generate in one day is 160,000 Wh or 160 kWh.
What factors impact how much solar panel production?
Solar panels are tested in standard test conditions (STC) which can be useful but not totally accurate. If you bought solar panels that can produce 400 watts per hour, this number came from lab testing standards.
Standard test conditions are typically at 77ºF, do not factor wind or weather and do not factor potential obstructions — such as clouds, dust, leaves or snow. Your real world life is different from lab simulations, but other factors can impact solar panel production.
Other factors can include the type of solar panel materials, your roof’s orientation and slope, shade from trees or other buildings and dust and debris.
How much energy can a home solar panel system produce?
The U.S. Energy Information Administration found that the average annual amount of electricity purchased by an American household was 10,791 kilowatt-hours, or around 899 kWh per month. This study used numbers from American households in 2022.
To power an entire home during the day requires around 15-25 rooftop solar panels. If you want additional power at night or on rainy days, a storage battery can store unused solar energy for later usage.
The solar-plus-storage system is best for helping homeowners power all or most of their households’ energy needs. However, it’s always a good idea to have your home connected to the electrical grid for more flexibility.
Solar-only systems are also good options for saving money, but will require you to draw from the electrical grid at night, on rainy days or at times of high usage.
Enact generates free custom solar proposals for homeowners across the U.S. Each system is custom designed for a customer’s home energy needs, rooftop and budget. Because Enact designs personalized solar systems, Enact customers have seen their utility bills shrink by 75% or more after going solar.
Can I power my home with solar panels?
A home solar panel can produce enough energy to power all or most of a home’s energy needs.
Powering your home with solar panels is a viable and environmentally friendly option for many American homeowners.
Enact customers have seen their residential utility bills shrink by 75% or more. The best way to power your home through solar is with a solar plus storage system. Solar plus storage systems include energy storage batteries, which store unused, low-cost solar energy for later use. This allows you to rely on your own power at night or on a rainy day — and avoid using the power grid.
To determine if solar is right for you, schedule a free consultation with an Enact energy advisor. Our friendly team of advisors will help assess your home’s energy needs, your roof structure and create a custom plan for your home.
Once you find the design that works best for you, Enact will coordinate your entire solar installation journey with a local installer partner. Through Enact, homeowners have access to custom solar quotes, choice in equipment and financing options and a transparent transition to clean energy.
Overall, with careful consideration and professional guidance, you can harness solar power to meet your home’s energy needs, contributing to both cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
What happens if my solar panels produce too much electricity?
Sometimes your solar panel system might produce more electricity than your home uses. Solar energy has to be used, stored in a battery or sent to the power grid. This scenario showcases the benefits of a grid-tied solar system with net metering. Net metering allows you to receive credits for the surplus energy your solar panels feed into the grid during sunny periods.
During times when your solar panels generate more electricity than your home needs, the excess is exported to the grid, and your utility company typically provides credits on your energy bill. These credits can offset the costs when your home requires electricity from the grid, such as during cloudy days or at night.
Not every state or utility company offers net metering incentives, but even without net metering — solar can still be beneficial to homeowners through energy storage.
Some homeowners opt for energy storage solutions like batteries. Excess solar energy can be stored in batteries during peak production times and utilized when solar generation is lower. This approach enhances energy independence and ensures a continuous power supply, even when sunlight is not available. Plus the more of your own you use through batteries, the less you need from the utility company.
Producing too much electricity with your solar panels offers opportunities for financial savings through net metering or increased self-sufficiency with energy storage solutions, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy strategy for your home.
Enact designs custom solar systems for our customers — we can help you get clean energy, energy storage and an electric vehicle charging station for your home. Schedule a free consultation to see how Enact can help you.


