For homeowners thinking of going solar — you can benefit under a Time-of-Use plan by producing your own electricity during the day. Electricity is often cheaper at night, when solar panels do not produce electricity.
Enact helps homeowners understand how a residential solar system can benefit them with our software solution. Regardless of your utility pricing type, solar offers homeowners financial and environmental benefits.
What is a Time-of-Use (TOU) Rate?
Electricity is generally more expensive during peak demand times and cheaper during off-peak hours. Rates might be higher in the afternoon and early evening when demand is highest and lower late at night or early in the morning when demand drops.
Demand is typically higher in the afternoons and evenings as people come home from school and work. This is typically when most people use more energy, such as watching TV, cooking, laundry or charging their electric vehicles.
What are Peak Hours?
Under a Time-of-Use billing system, the price of electricity increases during “peak hours.” Peak hours, also called “on-peak hours,” are pre-determined by your utility company. These hours are determined to match times when there is increased demand for electricity.
Peak hours are typically in the afternoon and evening — and during summer. These times match when more people are using electricity. During peak hours, utility companies use additional resources to generate more electricity.
TOU rates are designed to encourage customers to use electricity during periods of low-demand — such as at night or in the morning. This helps reduce operating costs for the utility company and can provide transparency into the costs of generating electricity.
Homeowners with solar panel systems can offset higher bills by generating their own electricity. Solar panels produce clean energy during the daytime and reduce dependence on the utility grid. Homeowners with a home battery system are also encouraged to use energy from their system during on-peak hours.
What are Off Peak Hours?
Off-peak hours are simply the times of day with lower costs of electricity due to lower demand. Typically, off-peak hours occur at night, in the morning and during winter. Lower costs of electricity encourages homeowners to perform high usage tasks during these times. These hours can be the best time for homeowners to wash dishes, do laundry and charge their EV.
For homeowners with a home battery system, it’s recommended to charge your batteries during off-peak hours — if you’re not using solar to charge your storage battery.
Examples of Time-of-Use Rates
- Off-Peak Hours: $0.12 per kWh from 7 PM – 1 PM
- Mid-Peak Hours: $0.22 per kWh from 1 PM – 3 PM
- Peak Hours: $0.32 per kWh from 3 PM – 7 PM
For some Time-of-Use plans, such as Xcel Energy’s plan in Colorado, weekends and select holidays are billed at off-peak hour prices.
These rates can also change seasonally, with higher rates during summer months when air conditioning use spikes and lower rates in winter.
Another example of Time-of-Use rates below comes from the Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E), which services Northern and Central California. PG&E is the largest electrical provider in California. Below is an example of PG&E’s seasonal schedule for its TOU rates.
Seasonal Variations in Time-of-Use Rates
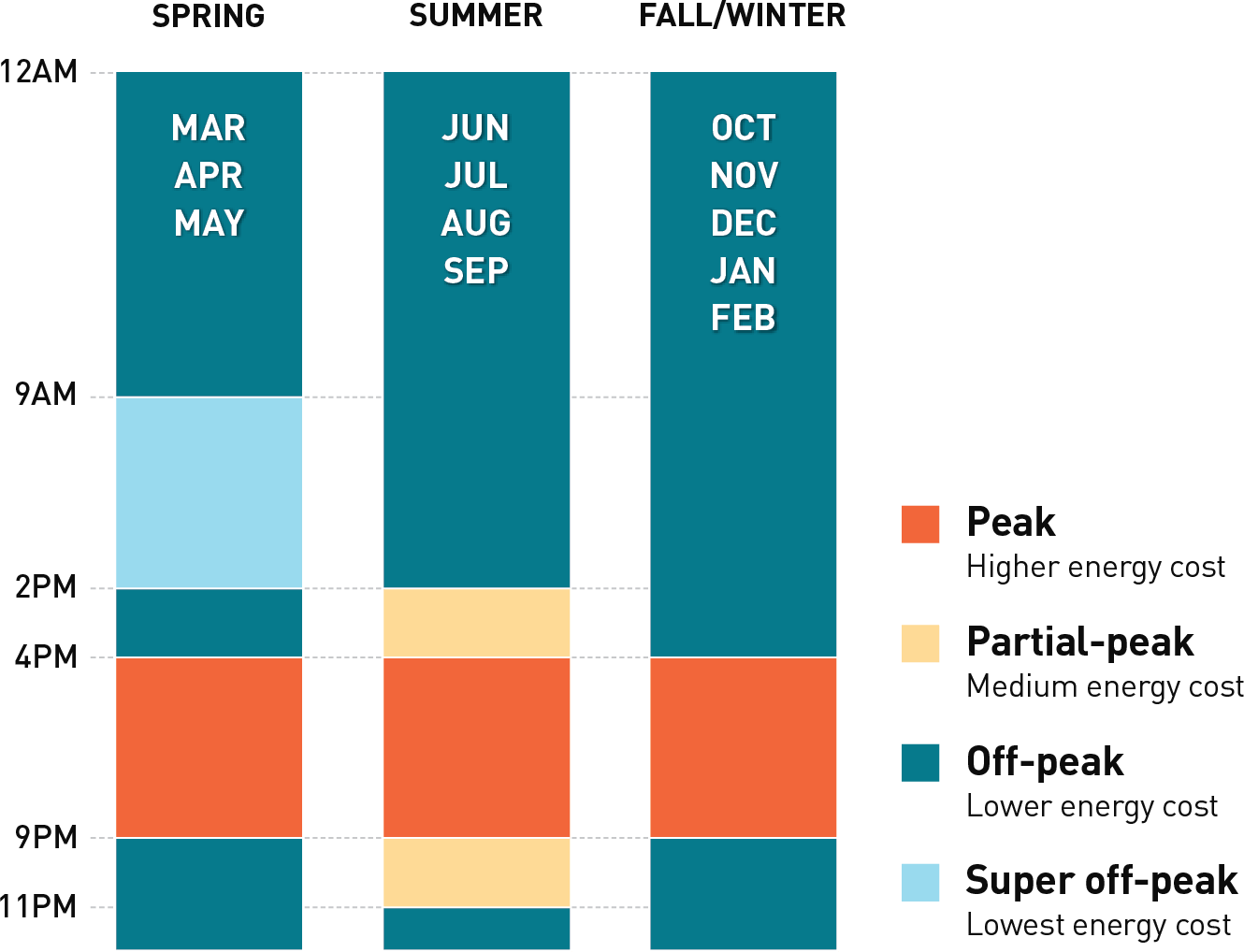
Summer vs. Winter Rates
For solar homeowners, this means that the value of the electricity generated by their panels can be higher in the summer. Thankfully, solar panel systems generate more electricity in the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. The higher energy yield can offset the cost of air conditioning.
What is the Purpose of Time-of-Use Rates?
Typically, the demand for electricity increases over the course of the day, peaking in the afternoon and evening. This increase corresponds with businesses opening, people going to work or school and other human activities.
Time-of-Use rates can encourage consumers to shift their electricity use to off-peak times, reducing strain on the grid during peak periods. Utilities can better manage demand and lower their operational costs. For consumers, shifting usage to off-peak times can lead to substantial savings on their electricity bills.
How Time-of-Use Rates Impact Homeowners

For example, running high-energy appliances like dishwashers, washing machines and electric vehicle chargers during off-peak hours can lead to substantial savings. Homeowners can also benefit from smart home technologies that automate energy use based on TOU schedules.
Seasonal variations in TOU rates, such as higher rates in summer due to increased air conditioning use, mean that homeowners must also consider the time of year when planning their energy use. Thankfully, solar panel systems produce electricity throughout the day — especially at the hottest parts of the day, which can lower the costs of air conditioning.
Those with energy storage systems can store excess solar power generated and use it during peak periods. This maximizes savings and provides a backup power source during outages. Battery owners can also charge their battery from the grid during off-peak hours. for later use.
TOU rates encourage more efficient energy use and can lead to significant cost savings for homeowners who adjust their habits and leverage solar energy.
How Solar Homeowners Can Benefit Under A Time-of-Use Rate?
Excess solar energy produced during these times can often be sold back to the grid at higher rates, further enhancing savings through net metering programs. Net metering policies can vary by state and utility company.
Peak Production vs. Peak Usage
Solar panels generate the most electricity during daylight hours, particularly in the late morning and early afternoon. Typically, peak production occurs before periods of high electricity demand, known as peak hours, when TOU rates are the highest. Peak usage for many families — and the broader power grid — tends to be in the late afternoon and early evening.
Energy Storage and Time-of-Use Rates
Adding an energy storage system, like a battery, to your solar setup can further optimize your savings under TOU rates. Here’s how:
Storing Excess Energy
Batteries allow you to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use during peak periods when rates are highest. Instead of exporting all your surplus power to the grid, you can use it to reduce or even eliminate your reliance on electricity from the utility grid.
This can significantly increase your savings, as you are essentially using your stored solar energy during higher cost times. With a battery, homeowners can continue to use low-cost solar energy toward the end of peak hours, when the sun may be going down.
For battery owners without solar, you can charge your battery during off-peak hours and use it during peak hours to save on electricity. A storage battery can reduce the cost of higher electricity rates for day-to-day use.
Enhanced Net Metering Benefits
In some cases, batteries can enhance the benefits of net metering. By strategically using stored energy to minimize grid consumption during peak periods and maximizing exports when rates are highest, you can make the most of the net metering credits. Advanced battery systems can be programmed to discharge stored energy at optimal times, aligning with your utility’s TOU schedule.
This is especially true for California homeowners impacted by the state’s NEM 3.0 policy. NEM 3.0 reduced the benefits solar homeowners received for exporting surplus energy to the utility grid. Enact found — despite the reduction — our customers continued to benefit from solar with energy storage under the new policy.
How to go Solar with Enact
Enact offers homeowners choice and transparency in the solar process. After scheduling a free consultation with an Enact home advisor, homeowners will receive a free custom proposal for a solar energy system. A home advisor uses Enact’s software platform to design a custom system that will meet your home’s energy needs.
An Enact Solar Proposal will include detailed information regarding your solar system specifications, expected energy production and forecasted financial savings. Additionally, Enact offers upfront, transparent pricing without hidden fees. Enact accepts a wide variety of payment and financing options.
After agreeing on the right proposal for your home, Enact coordinates the installation process with a trusted installer partner. Our goal is to simplify the solar installation process for homeowners, while offering choice.
Enact offers homeowners ongoing monitoring and support through the Enact Home app. With Enact, homeowners continue to provide detailed reports, help troubleshoot any issues and track the system’s long-term performance and financial outcomes.
To get started with a free, custom proposal for your home — sign up for a consultation with an Enact home advisor. Enact consultations are free and require no obligations.


