Electrical Grid
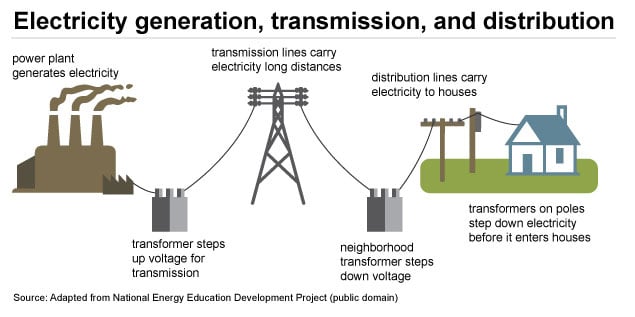
The Grid is the worldwide, interconnected system of power lines, sub-stations, transformers, and many of the other needed ingredients that are responsible for transporting electrical energy from the sources of production to the end-users. Such an intricate system is the backbone of the modern society powering homes, businesses, and industries. Electricity producers – everything from large-scale power plants (using fossil fuels, nuclear, or renewables such as hydro and wind), to distributed solar installations – pump power into this network. This electricity is then transmitted over long distances at high voltage, and transmitted at low voltage to the consumers. Its stability and reliability come in first place and it has to deal with ever-present issues such as aging infrastructure and balancing the intermittent renewables like solar, and ramping up and down to match erratic demand. For owners of solar systems, the grid was and continues to be a source of power during periods when solar generation is insufficient and a consumption point for excess solar over net metering programs.